Diversion wells
Information taken from:
Swatara Creek Diversion Wells - Pictures of successful limestone diversion wells on a Swatara Creek tributary.
DEP - The science of AMD and passive treatment
Diversion wells add alkalinity to waters that have low pH and low dissolved metal concentrations.
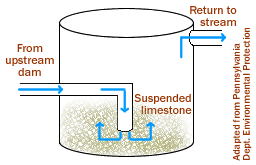
In a diversion well, acidic water falls vertically through a pipe from an upstream dam into a downstream "well" that contains crushed limestone. The drastic drop in elevation gives the water enough force to suspend limestone gravel located at the bottom of the well, creating a "fluidized bed." This churning limestone gravel crushes itself, increasing its neutralization ability and preventing armoring (the coating of limestone with iron oxide from the AMD).
The water, now with higher alkalinity, flows upward and overflows the well, where it is diverted back into the stream. Some of the pieces of limestone are also carried up out of the well and enter the stream, where they line the stream bed to continue neutralizing acid.
Operations & Maintenance Considerations
Diversion wells have to be refilled with clean limestone approximately every two weeks.